You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection (2016)

1. Introduction
기존의 R-CNN 계열의 detection 모델들은 localization과 classification 파트가 분리 되있는 2-stage-detector였지만 YOLO는 bounding box 예측과 classificaion을 동시에 수행하는 1-stage-detector를 제시하였다.
YOLO의 장점은 다음과 같다.
- Object detection을 regression 문제로 변환해 단순화 하여 실시간으로 detection이 가능해졌다. (엄청나게 빠른 속도)
- 기존 detection 방식은 예측된 bounding box 내부만을 이용해서 클래스를 예측하는데 YOLO는 전체 이미지를 통해 bounding box의 class를 예측한다.
- 학습한 이미지에 대한 예측 뿐 아니라 다른 도메인의 이미지에도 어느정도 괜찮은 성능을 보였다.
하지만 당시 새로 나온 구조라서 그런지 YOLO v1은 단점도 적지않은데 단점은 아래에서 나올 것이다.
2. Unified Detection
위에서 언급한 것 처럼 YOLO v1에서는 end-to-end 방식으로 하나의 convolution network를 거쳐서 마지막 feature_map에서 bounding box와 class를 예측한다.
모델의 최종 feature map은 7 x 7 x 30의 사이즈를 가지고 있게 되고 이것을 49개의 영역의 grid cell로 보고 각 grid cell에서 2개의 bounding box와 class를 예측을 하게 된다.
즉 7 x 7 x 30 의 의미는 다음과 같다.
- 7 x 7 x 30 == S x S x (5 x B + C)
- S = feature size : 7
- 5 = (cx, cy, w, h, conffidence)
- B = number of boxes : 2
- C = classes : 20 (PASCAL VOC dataset)
yolo의 conffidence score는 Pr(Object) x IOU 로 물체가 있을 확률과 실제 물체의 bounding box와 예측 bounding box와의 iou를 곱해서 구하게 된다.
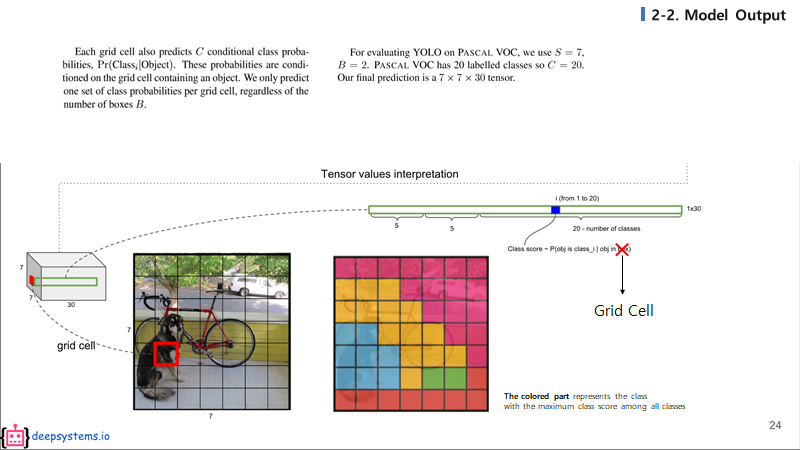
각 grid cell 하나하나는 20개의 클래스에 대한 예측 값들을 가지게 된다. 위 그림의 grid cell을 여러가지의 색으로 구분한 그림을 보자. 서로 다른 색은 서로 다른 클래스이고, 각 그리드 셀에서 가장 높게 예측된 클래스의 색을 칠하면 위와 같은 그림이 나올 것이다.
2-1. Network Design

YOLO v1은 GoogLeNet의 네트워크 구조를 모티브로 하였고 총 24개의 conv layer와 2개의 FC layer를 포함하고 있다. GoogLeNet의 inception을 가져와 1x1 conv를 활용하여 연산량을 줄이려고 하였고 그 외의 모든 conv layer에서는 3x3 filter만 사용하였다.
참고로 논문에서는 왼쪽 20개의 conv layer는 GoogLeNet을 이용하여 ImageNet classification에 사용된 weight를 가져와 fine tuning하였는데 구현 코드에서는 그냥 처음부터 학습을 시켰다.
2-2 Training
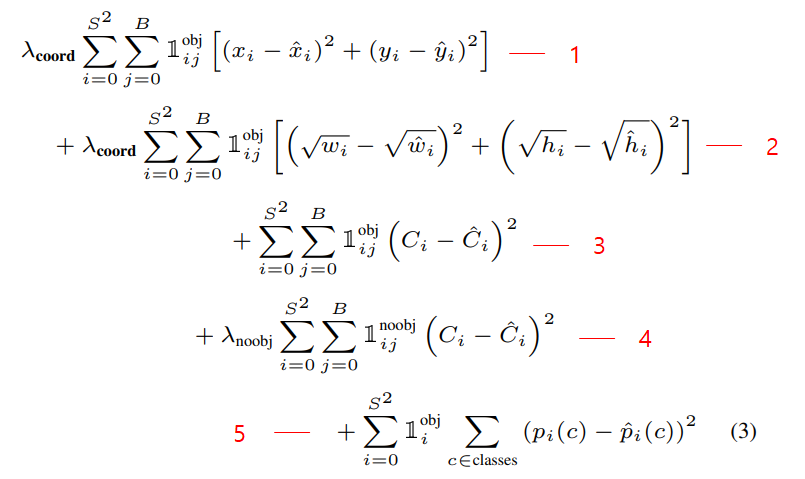
YOLO v1은 위와같은 Multi Loss를 사용하였다. 특이한 점은 CrossEntropy가 아닌 SSE(Sum Square Error)를 사용했다는 것인데 구간별로 천천히 살펴보자
lambda_coord : 5
lambda_noobj : 0.5
- Localization loss : x, y값을 regression하는 SSE loss
- Localization loss : width, height값은 regression하는 SSE loss
- Confidence loss : object가 있는 곳의 confidence SSE loss
- Confidence loss : object가 없는 곳의 confidence SSE loss
- Classification loss : object가 있는 곳의 각 class별 SSE loss (각 셀당 1개의 class probability가 나오므로 ij가 아닌 i뿐)
참고로 loss를 구하기 전에 미리 ground truth쪽 confidence와 해당 클래스의 인덱스에 1을 할당해준다.
2-3 Inference
테스트할 때, 성능을 확인하기 위해서 최종적인 bounding box를 예측해야 한다.

첫번째로 ouput 에서 예측된 bbox의 confidence score와 class score를 곱한다.
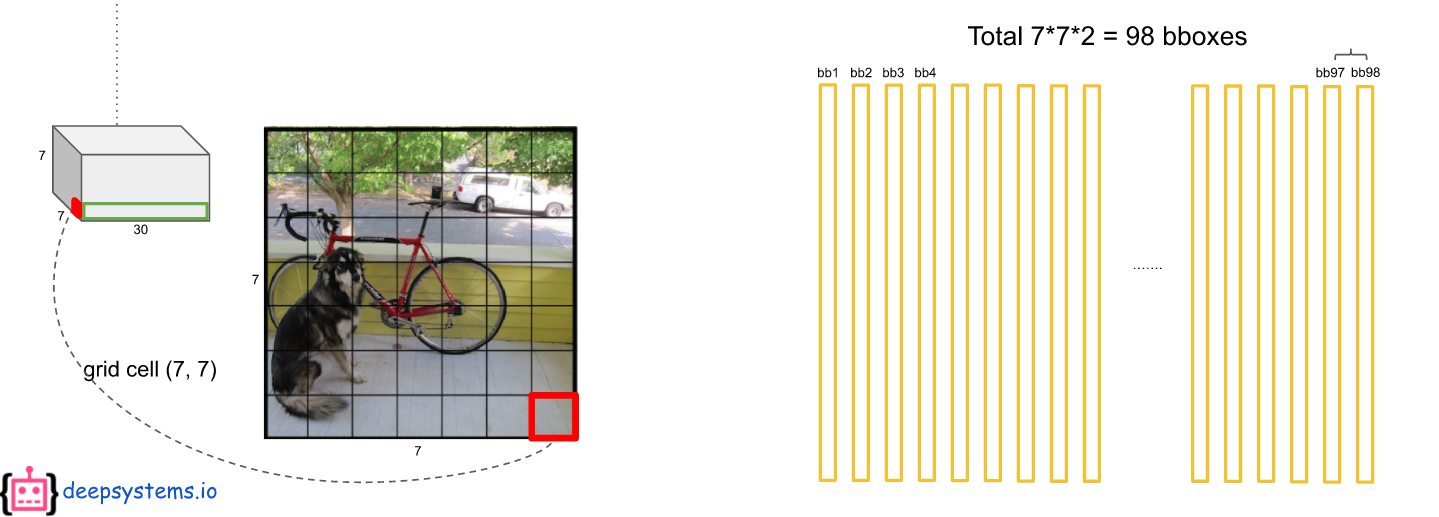
7 x 7의 각 grid cell에 2개의 bbox를 예측하므로 총 98개의 막대(20 x 1 벡터)가 나오게 된다. 그러면 최종적으로 98 x 20 = 1440개의 값이 나오는데 이것을 어떻게 처리해야 한 물체에 하나의 bbox가 나오게 될까?

먼저 1440개의 값중에 0.2(Threshold)보다 작은 값들은 모두 0으로 만든다. 그 후에 클래스별로 내림차순으로 정렬을 하고 NMS 기법을 통해서 최종 detection output을 만들어 낸다. NMS는 아래 포스팅에서 자세히 다뤘으니 넘어가겠다.
NMS(Non Max Suppression)
NMS(Non Max Suppression) 이번 포스팅 에서는 IOU에 이어서 NMS(Non Max Suppression)에 대해 알아보려고 한다. NMS는 여러 Object Detection논문(YOLO, SSD 등)에서 사용한 방법으로 각각의 물체에 대한 bound..
visionhong.tistory.com
모든 클래스에 대해 NMS을 적용하면 대부분의 값들이 0으로 만들어 질 것이다.
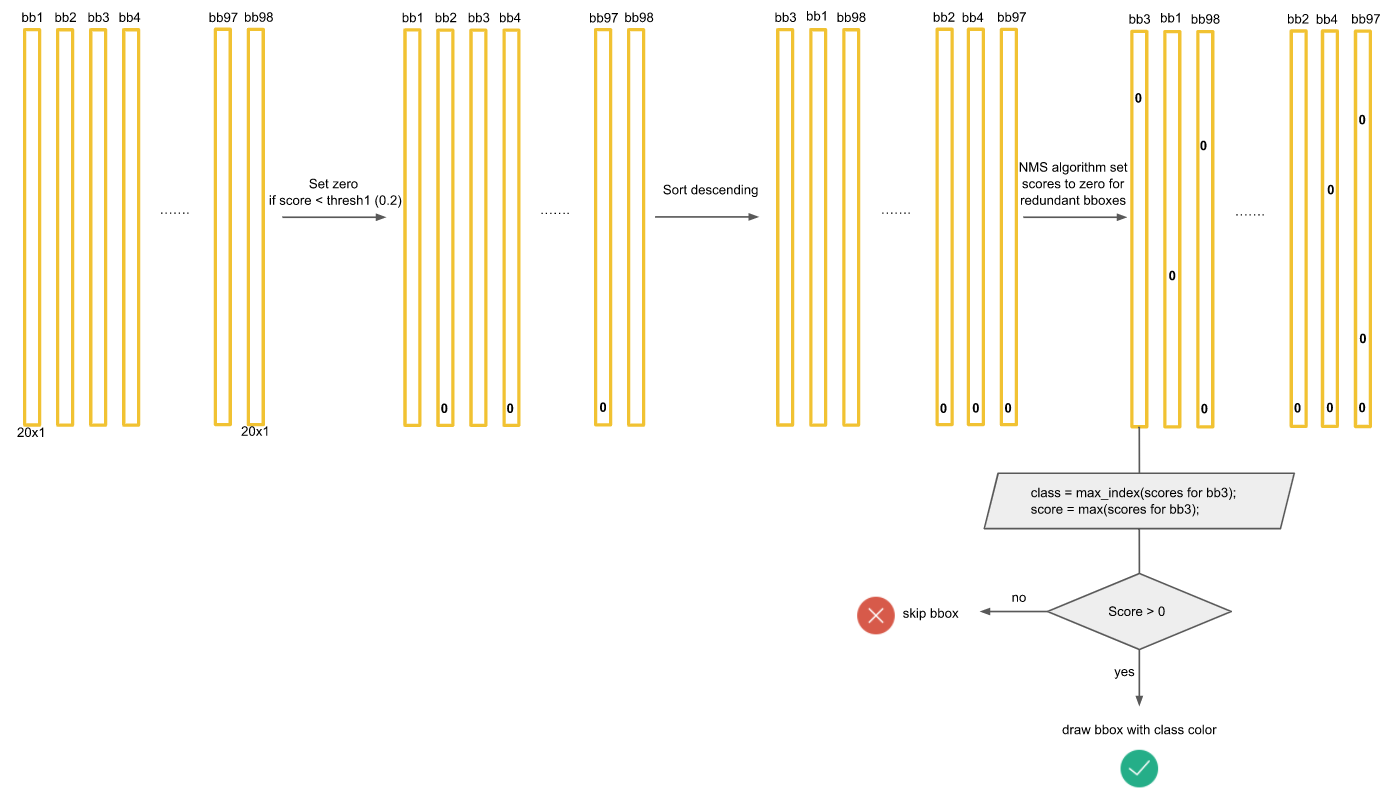
마지막으로 각 bbox에 대해서 가장 크게 예측되고 0보다 큰 클래스만 뽑아내면 아래와 같이 몇개의 막대만 살아남게되고 이것이 최종 output이 된다.

2.4 Limitations of YOLO
- YOLO는 1개의 grid cell당 1개의 class만 취급하기 때문에 2개 이상의 물체들의 중심이 한 grid cell에 모여있더라도 한가지의 class만 예측할 수 있다. 그렇다는 것은 새 떼와 같은 작은 물체들이 모여있을때 감지를 하지 못하게 된다.
- 일정한 비율의 bbox로만 예측을 하다보니 색다른 비율을가진 물체에 대한 예측이 좋지 못하다. -> 일반화가 어려움
- 작은 bbox의 loss와 큰 bbox의 loss를 동일하게 처리한다. -> 큰 상자의 작은 움직임에 비해 작은 상자의 작은 움직임은 훨씬 더 큰 형향을 끼치기 때문
이러한 단점들로 인해 YOLO v1의 속도는 엄청 빠르지만 반면에 정확도가 SOTA에 비해 낮았다.
3. Experiments
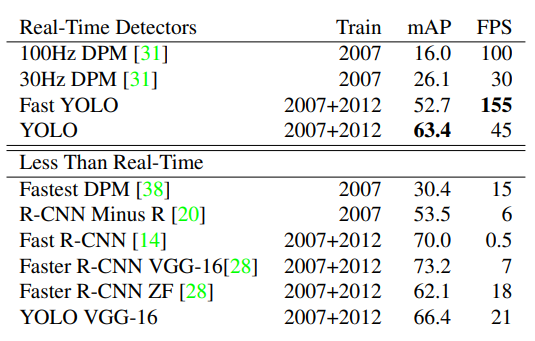
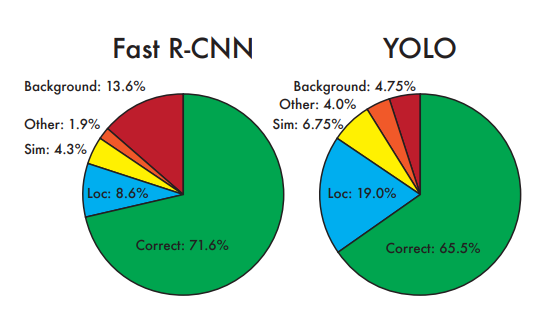

4. Conclusion
- one stage detector로서 엄청 빠르다. (Real Time Object Detection)
- 다른 도메인에서도 빠르고 나름 괜찮은 성능을 보인다.
- 하지만 단점이 많다. (YOLO v2 부터 많은 개선이 일어남)
Pytorch 구현(Colab)
!mkdir train
!mkdir test
!wget http://pjreddie.com/media/files/VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.tar -P train/
!wget http://pjreddie.com/media/files/VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tar -P test/
!tar -xf test/VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tar -C test/
!tar -xf train/VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.tar -C train/
!rm -rf test/VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tarPASCAL VOC 2007 데이터를 train, test 폴더를 만들어서 받아온다.
!pip install xmltodict
!pip install -U albumentationsxml파일을 parsing하기 위해 xml라이브러리 대신 xmltodict이라는 라이브러리를 설치
augmentation을 위한 albumentations 라이브러리 설치
root_dir = '/content'
annot_f = './{}/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations'
image_f = './{}/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/{}'
classes = ['person', 'bird', 'cat', 'cow', 'dog', 'horse',
'sheep', 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'boat', 'bus', 'car',
'motorbike', 'train', 'bottle', 'chair', 'dining table',
'potted plant', 'sofa', 'tv/monitor' ]
num_classes = len(classes)
feature_size = 7
num_bboxes = 2파일 경로와 PASCAL VOC class 정의
import sys
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.optim.lr_scheduler
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
## utils
import numpy as np
import random, math, time
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
## File Loader
import os, xmltodict
import os.path as pth
from PIL import Image
# Draw Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
## Transformer
from random import sample
import albumentations as A
from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensor
# Seed
random.seed(53)필요한 라이브러리, 모듈 import
def draw_image(image_info, w=448, h=448, transforms=None):
im = np.array(Image.open(image_f.format('train', image_info['image_id'])).convert('RGB').resize((w,h)), dtype=np.uint8)
# Create figure and axes
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(7,7))
bb = image_info['bboxs']
la = image_info['labels']
if transforms:
sample = transforms(image=im, bboxes=bb, category_ids=la)
im = sample['image'].permute(1,2,0).numpy()
bb = sample['bboxes']
la = sample['category_ids']
# Display the image
ax.imshow(im)
for b, l in zip(bb, la):
# top left (x, y) , (w, h)
rect = patches.Rectangle((b[0]*w,b[1]*h),(b[2]-b[0])*w,(b[3]-b[1])*h,linewidth=1,edgecolor='r',
facecolor='none')
# Add the patch to the Axes
ax.add_patch(rect)
props = dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='red', alpha=0.9)
plt.text(b[0]*w, b[1]*h, classes[l], fontsize=10, color='white', bbox=props)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()시각화

def get_infos(annot_f=annot_f, mode='train'):
annot_dir = annot_f.format(mode)
result = []
for ano in [pth.join(annot_dir, ano) for ano in os.listdir(annot_dir)]:
f = open(ano) # xml 파일 하나씩 읽어들임
info = xmltodict.parse(f.read())['annotation']
image_id = info['filename']
image_size = np.asarray(tuple(map(int, info['size'].values()))[:2], np.int16)
w, h = image_size
box_objects = info['object']
labels = []
bboxs = []
for obj in box_objects:
try:
labels.append(classes.index(obj['name'].lower())) # 0~19 사이
bboxs.append(tuple(map(int, obj['bndbox'].values())))
except: pass
# Resizing Box, Change x1 y1 x2 y2
# albumentations (normalized box)
bboxs = np.asarray(bboxs, dtype=np.float64)
try:
bboxs[:, [0,2]] /= w
bboxs[:, [1,3]] /= h
except: pass
if bboxs.shape[0] or mode=='test':
result.append({'image_id':image_id, 'image_size':image_size, 'bboxs':bboxs, 'labels':labels})
return result
trval_list = get_infos()
test_list = get_infos(mode='test')
len(trval_list), len(test_list)xml파일을 읽어서 필요한 정보만 parsing해서 딕셔너리를 감싼 리스트로 반환
len(traval_list) = 3067
len(traval_list) = 4952
def get_tv_idx(tl, k=0.5):
total_idx = range(tl) # (0,3067)
train_idx = sample(total_idx, int(tl*k)) # 3067/2 개만큼 뽑음
valid_idx = set(total_idx) - set(train_idx) # 안뽑힌 index들이 valid_idx
return train_idx, list(valid_idx)
train_idx, valid_idx = get_tv_idx(len(trval_list))
trval_list = np.asarray(trval_list) # list -> array
train_list = trval_list[train_idx]
valid_list = trval_list[valid_idx]
len(train_list), len(valid_list), len(test_list)traval_list 파일을 train, valid set으로 나누어주는 함수
class VOCDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_list, mode='train', transforms=None):
self.data_list = data_list
self.mode = mode
self.transforms = transforms
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
record = self.data_list[idx]
img_id = record['image_id']
bboxs = record['bboxs']
labels = record['labels']
img = Image.open(image_f.format(self.mode, img_id)).convert('RGB')
img = np.array(img)
if self.transforms:
for t in self.transforms:
sample = self.transforms(image=img, bboxes=bboxs, category_ids=labels)
image = sample['image']
bboxs = np.asarray(sample['bboxes'])
labels = np.asarray(sample['category_ids'])
if self.mode== 'train':
target = encode(bboxs, labels)
return image, target
else:
return image사용자 정의 Dataset
def encode(bboxs, labels):
S = feature_size
B = num_bboxes
N = 5 * B + num_classes
cell_size = 1.0 / float(S)
box_cxy = (bboxs[:, 2:] + bboxs[:, :2]) / 2.0
box_wh = (bboxs[:, 2:] - bboxs[:, :2])
target = np.zeros((S,S,N))
for b in range(bboxs.shape[0]): # gt박스 수만큼 반복
cxy, wh, label = box_cxy[b], box_wh[b], labels[b]
ij = np.ceil(cxy / cell_size) -1.0 # ceil -> 소수점있으면 무조건 올림 4.1 -> 5
i,j = map(int, ij) # i,j는 셀 번호 0~6
top_left = ij*cell_size # 각 셀의 좌상단 좌표
dxy_norm = (cxy-top_left) / cell_size
for k in range(B): # 한 셀당 두개의 박스
target[i, j, 5*k:5*(k+1)] = np.r_[dxy_norm, wh, 1] # confidence에 1
target[j, i, 5*B+label] = 1.0 # 해당label에 1
return target
# target data에 대한 encoding을 하는 함수
target (7 x 7 x 30) 에서 물체의 담당 셀의 정보(confidence, class index)에 1 나머지는 0으로 만들어줌
def get_train_transforms():
return A.Compose([
A.Resize(448,448, always_apply=True, p=1),
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.2),
A.HorizontalFlip(),
ToTensor(),
],bbox_params = A.BboxParams(format='albumentations', label_fields=['category_ids']))
def get_test_transforms():
return A.Compose([
A.Resize(448, 448, always_apply=True, p=1),
ToTensor(),
])albumentations을 사용하여 transform 정의
albumentationd은 bbox의 변환도 알아서 같이 해주는 미친 라이브러리!
train_ds = VOCDataset(train_list, transforms=get_train_transforms())
valid_ds = VOCDataset(valid_list, transforms=get_test_transforms())
test_ds = VOCDataset(test_list, mode='test', transforms=get_test_transforms())
# torch tensor를 batch size만큼 묶어줌
def collate_fn(batch):
images, targets = zip(*batch)
return torch.cat([img.reshape(-1, 3, 448, 448) for img in images], 0), torch.FloatTensor(targets)
def test_collate_fn(batch):
images = batch
return torch.cat([img.reshape(-1, 3, 448, 448) for img in images], 0)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, collate_fn = collate_fn)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, collate_fn = collate_fn)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, collate_fn = test_collate_fn)
DataLoader 정의
class YOLO_v1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=20, num_bboxes=2):
super(YOLO_v1, self).__init__()
self.feature_size = 7
self.num_bboxes = num_bboxes
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=4),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(192),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
Flatten(),
nn.Linear(in_features=7*7*1024, out_features=4096),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=(feature_size*feature_size*(5*num_bboxes+num_classes))),
nn.Softmax()
)
self.init_weight(self.conv)
self.init_weight(self.fc)
def forward(self, x):
s,b,c = self.feature_size, self.num_bboxes, self.num_classes
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.fc(x)
x = x.view(-1, s, s, (5 * b + c))
return x
def init_weight(self, modules):
for m in modules:
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='leaky_relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
class Squeeze(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Squeeze, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x.squeeze()
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Flatten, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.size(0), -1)YOLO v1 모델 정의
def compute_iou(bbox1, bbox2):
'''
Compute the IOU (Intersection over Union) of two set of bboxes, each bbox format: [x1,y1,x2,y2]
:param bbox1: (Tensor) bounding boxes, sized [N,4]
:param bbox2: (Tensor) bounding boxes, sized [N,4]
:return: (Tensor) IoU, sized [N, M].
'''
N = bbox1.size(0)
M = bbox2.size(0)
# Compute left-top coordinate of the intersections
lt = torch.max(
bbox1[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N,2] -> [N,1,2] -> [N,M,2]
bbox2[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2) # [M,2] -> [1,M,2] -> [N,M,2]
)
# Compute right-bottom coordinate of the intersections
rb = torch.min(
bbox1[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N,2] -> [N,1,2] -> [N,M,2]
bbox2[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2) # [M,2] -> [1,M,2] -> [N,M,2]
)
# Compute area of the intersections from the coordinates
wh = rb - lt # width and height of the intersection, [N,M,2]
wh[wh < 0] = 0 # clip at 0
inter = wh[:, :, 0] * wh[:, :, 1] # [N,M]
# Compute area of the bboxes
area1 = (bbox1[:, 2] - bbox1[:, 0]) * (bbox1[:, 3] - bbox1[:, 1]) # [N,]
area2 = (bbox2[:, 2] - bbox2[:, 0]) * (bbox2[:, 3] - bbox2[:, 1]) # [N,]
area1 = area1.unsqueeze(1).expand_as(inter) # [N,] -> [N, 1] -> [N,M]
area2 = area2.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(inter) # [N,] -> [N, 1] -> [N,M]
# Compute IoU from the areas
union = area1 + area2 - inter
iou = inter / union
return iouIOU(Intersection Over Union)를 계산해주는 함수
def loss_fn(pred_tensor, target_tensor):
""" Compute loss for YOLO training.
Args:
pred_tensor: (Tensor) predictions, sized [n_batch, S, S, Bx5+C], 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf]).
target_tensor: (Tensor) targets, sized [n_batch, S, S, Bx5+C].
Returns:
(Tensor): loss, sized [1, ].
"""
S, B, C = feature_size, num_bboxes, num_classes
N = 5 * B + C # 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf]
lambda_coord = 5
lambda_noobj = 0.5
batch_size = pred_tensor.size(0)
coord_mask = target_tensor[:, :, :, 4] > 0 # mask for the cells which contain objects. [n_batch, S, S]
noobj_mask = target_tensor[:, :, :, 4] == 0 # mask for the cells which not contain objects [n_batch, S, S]
coord_mask = coord_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor) # [n_batch, S, S] -> [n_batch, S, S, N]
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor) # [n_batch, S, S] -> [n_batch, S, S, N]
coord_pred = pred_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N) # pred tensor on the cells which contain objects. [n_coord, N]
# n_coord: numver of the cells which contain objects.
bbox_pred = coord_pred[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5) # [n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
class_pred = coord_pred[:, 5*B:] # [n_coord, C]
coord_target = target_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N) # target tensor on the cells which contain objects. [n_coord, N]
bbox_target = coord_target[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5) # [batch*7*7*2, 5]
class_target = coord_target[:, 5*B:]
# Compute loss for the cells with no object bbox
noobj_pred = pred_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N) # [n_noobj, N]
noobj_target = target_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
noobj_conf_mask = torch.cuda.ByteTensor(noobj_pred.size()).fill_(0) # [n_noobj, N]
for b in range(B):
noobj_conf_mask[:, 4+B*5] = 1 # noobj_conf_mask[:, 4] = 1; noobj_conf_mask[:, 9] = 1
noobj_pred_conf = noobj_pred[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj, 2=len([conf1, conf2])]
noobj_target_conf = noobj_target[noobj_conf_mask]
# No object confidence loss (SSE)
loss_noobj = F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf, reduction='sum')
# Compute loss for the cells with objects
coord_response_mask = torch.cuda.ByteTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(0) # [n_coord x B, 5]
coord_not_response_mask = torch.cuda.ByteTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(1) # [n_coord x B, 5]
bbox_target_iou = torch.zeros(bbox_target.size()).cuda() # [n_coord x B, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
# Choose the predicted bbox having the highest IoU for each target bbox
for i in range(0, bbox_target.size(0), B):
pred = bbox_pred[i:i + B] # predicted bboxes at i-th cell, [B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
pred_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(pred.size())) # [B, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=pred[:, 2] and (w,h)=pred[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
pred_xyxy[:, :2] = pred[:, :2] / float(S) - 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
pred_xyxy[:, 2:4] = pred[:, :2] / float(S) + 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
target = bbox_target[
i] # target bbox at i-th cell. Because target boxes contained by each cell are identical in current implementation, enough to extract the first one.
target = bbox_target[i].view(-1, 5) # target bbox at i-th cell, [1, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
target_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(target.size())) # [1, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=target[:, 2] and (w,h)=target[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
target_xyxy[:, :2] = target[:, :2] / float(S) - 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
target_xyxy[:, 2:4] = target[:, :2] / float(S) + 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
iou = compute_iou(pred_xyxy[:, :4], target_xyxy[:, :4]) # [B, 1]
max_iou, max_index = iou.max(0)
max_index = max_index.data.cuda()
coord_response_mask[i + max_index] = 1
coord_not_response_mask[i + max_index] = 0
# "we want the confidence score to equal the intersection over union (IOU) between the predicted box and the ground truth"
# from the original paper of YOLO.
bbox_target_iou[i + max_index, torch.LongTensor([4]).cuda()] = (max_iou).data.cuda()
bbox_target_iou = Variable(bbox_target_iou).cuda()
# BBox location/size and objectness loss for the response bboxes.
bbox_pred_response = bbox_pred[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5]
bbox_target_response = bbox_target[coord_response_mask].view(-1,
5) # [n_response, 5], only the first 4=(x, y, w, h) are used
target_iou = bbox_target_iou[coord_response_mask].view(-1,
5) # [n_response, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
loss_xy = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, :2], bbox_target_response[:, :2], reduction='sum')
loss_wh = F.mse_loss(torch.sqrt(bbox_pred_response[:, 2:4]), torch.sqrt(bbox_target_response[:, 2:4]),
reduction='sum')
loss_obj = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, 4], target_iou[:, 4], reduction='sum')
# Class probability loss for the cells which contain objects.
loss_class = F.mse_loss(class_pred, class_target, reduction='sum')
# Total loss
loss = lambda_coord * (loss_xy + loss_wh) + loss_obj + lambda_noobj * loss_noobj + loss_class
loss = loss / float(batch_size)
return lossloss를 구해주는 Loss Function 함수
yolo = YOLO_v1().cuda()
init_lr = 0.001
base_lr = 0.01
optimizer = optim.SGD(yolo.parameters(), lr=init_lr, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)
def update_lr(optimizer, epoch, burnin_base, burnin_exp=4.0):
if epoch in range(50):
lr = init_lr + (base_lr - init_lr) * math.pow(epoch/(50-1), burnin_exp)
elif epoch == 50:
lr = base_lr
elif epoch == 750:
lr = 0.001
elif epoch == 1050:
lr = 0.0001
else:
return
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr모델 인스턴스 생성, optimizer정의, Learning rate schedule 함수
start_time = time.time()
bl = len(train_loader) # 48
history = {'total_loss':[]}
for epoch in range(150):
tk0 = tqdm(train_loader, total=bl, leave=False)
t_loss = 0.0
breaking=False
for step, (image, target) in enumerate(tk0):
image, target = image.to(device), target.to(device)
update_lr(optimizer, epoch, float(step) / float(bl - 1))
output = yolo(image)
loss = loss_fn(output, target).cuda()
if math.isnan(loss):
print(loss)
breaking = True
break
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
t_loss += loss.item()
history['total_loss'].append(loss.item())
if breaking:
break
# print statistics
tqdm.write(f'[EPOCH : {epoch+1} total_loss: {t_loss/bl} Total_elapesd_time: {(time.time()-start_time)/60}분')
state = {'epoch': epoch,
'model': yolo,
'optimizer': optimizer}
filename = 'checkpoint_yolov1.pth.tar'
torch.save(state, filename)
print(time.time() - start_time)
print('Finished Training')
Training 진행 (80 epoch까지 약 1시간 30분걸렸음)
def decode(pred_tensor):
'''
Decode tensor into box coordinates, class labels, and probs_detected.
Args:
pred_tensor: (tensor) tensor to decode sized [S, S, 5 x B + C], 5=(x, y, w, h, conf)
Returns:
boxes: (tensor) [[x1, y1, x2, y2]_obj, ...]. Normalized from 0.0 to 1.0 w.r.t. image width/height, sized [n_boxes, 4].
labels: (tensor) class labels for each detected box, sized [n_boxes]
confidences: (tensor) objectness confidences for each detected box, sized [n_boxes].
class_score: (tensor) scores for most likely class for each detected box, sized [n_boxes,].
'''
S,B,C = feature_size, num_bboxes, num_classes
conf_thresh = 0.1
prob_thresh = 0.1
nms_thresh = 0.5
boxes, labels, confidences, class_scores = [], [], [], []
cell_size = 1.0 / float(S)
conf = pred_tensor[:,:,4].unsqueeze(2) # [7, 7, 1]
for b in range(1,B):
conf = torch.cat((conf, pred_tensor[:,:,5*b+4].unsqueeze(2)), 2)
conf_mask = conf > conf_thresh # [S, S, B]
# TBM, further optimization may be possible by replacing thre following for-loops with tensor opterations.
for i in range(S): # for x-dimension.
for j in range(S): # for y_dimension.
class_score, class_label = torch.max(pred_tensor[j, i, 5*B:], 0) # 해당 셀에서 가장 높은 class score
for b in range(B):
conf = pred_tensor[j, i, 5*b+4]
prob = conf * class_score
if float(prob) < prob_thresh:
continue
# Compute box corner (x1, y1, x2, y2) from tensor.
box = pred_tensor[j, i, 5*b : 5*b+4]
# cell left-top corner. Normalized from 0.0 to 1.0 w.r.t. image width/height
x0y0_normalized = torch.FloatTensor([i,j]) * cell_size
# box center. Normalized from 0.0 to 1.0 w.r.t. image width/height.
xy_normalized = box[:2] * cell_size + x0y0_normalized
# Box width and height. Normalized from 0.0 to 1.0 w.r.t. image width/height.
wh_normalized = box[2:]
box_xyxy = torch.FloatTensor(4) # [4,]
box_xyxy[:2] = xy_normalized - 0.5 * wh_normalized # left-top corner(x1, y1)
box_xyxy[2:] = xy_normalized + 0.5 * wh_normalized # right-bottom corner(x2, y2)
# Append result to the lists
boxes.append(box_xyxy)
labels.append(class_label)
confidences.append(conf)
class_score.append(class_score)
if len(boxes) > 0:
boxes = torch.stack(boxes, 0) # [n_boxes, 4]
labels = torch.stack(labels, 0) # [n_boxes]
confidences = torch.stack(confidences, 0) # [n_boxes]
class_score = torch.stack(class_score, 0) # [n_boxes]
else:
# If no box found, return empty tensors.
boxes = torch.FloatTensor(0, 4)
labels = torch.LongTensor(0)
confidences = torch.FloatTensor(0)
class_scores = torch.FloatTensor(0)
return boxes, labels, confidences, class_score예측결과 Tensor를 다시 boxes, labels, confidences, class_score로 decoding하는 함수
def test_visualize(images, outputs):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(7,7))
img = Image.open(image_f.format('test',test_list[0]['image_id']))
w,h = test_list[0]['image_size']
im = np.asarray(img)
ax.imshow(im)
for output in outputs:
b, l, c, sc = decode(output)
if b.shape[0]:
# patches.Rectangle(xy,width,height)
rect = patches.Rectangle((b[0]*w,b[1]*h),(b[2]-b[0])*w,(b[3]-b[1])*h,linewidth=1,edgecolor='r',facecolor='none')
ax.add_path(rect)
probs = dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='red', alpha=.9)
plt.text(b[0]*w, b[1]*h, '%s : %.2f'%(classes[l], sc), fontsize=10, color='white', bbox=props)
Test Visualization
Ending
이번 포스팅에서는 YOLO v1에대해 알아보았다. 지금을 기점으로 차근차근 논문 구현코드를 하나하나씩 뒤집어 엎어 볼 예정이다. 아직은 정말 너무 어렵지만 계속 나아갈 것이다. Keep going
reference
- Paper- arxiv.org/abs/1506.02640
- PPT - docs.google.com/presentation/d/1aeRvtKG21KHdD5lg6Hgyhx5rPq_ZOsGjG5rJ1HP7BbA/pub?start=false&loop=false&delayms=3000&slide=id.p
- Review- www.youtube.com/watch?v=eTDcoeqj1_w&t=1680s
- YOLO v1 pytorch Colab - wolfy.tistory.com/259?category=903250
- YOLO v1 pytorch Github - github.com/motokimura/yolo_v1_pytorch
'Deep Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [논문리뷰] Mobilenet v2 (0) | 2021.02.14 |
|---|---|
| [논문리뷰] YOLO v3 (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| Linear Regression (1) | 2021.01.26 |
| [논문리뷰] SSD : Single Shot Multibox Detector (2) | 2021.01.23 |
| mAP(Mean Average Precision) [2] (2) | 2021.01.21 |
